Introduction There are various processes for manufacturing pipes across industries. The two most popular pipe manufacturing techniques are seamless and electric resistance welded (ERW). Construction, water transportation, and oil and gas are among the businesses that employ these pipes. There are similarities between these pipes, including their shapes and functions. But there are certain differences,…
Introduction Carbon steel is widely used around the world these days. But only a small number of people know what it is and why it is very important. You usually find it in buildings, bridges, pipes, tools, vehicles, and even cookware. This article explains what carbon steel is, its advantages, and its disadvantages. It lastly…
Introduction Coatings play a key role in protecting pipeline systems. Pipelines move the fuels, water, chemicals, and industrial fluids that keep cities and industries running. Because of their underground structure, they are constantly exposed to harsh environments, which lead to corrosion, abrasion, rust, and more. This can weaken the structure, and repair can be costly. …
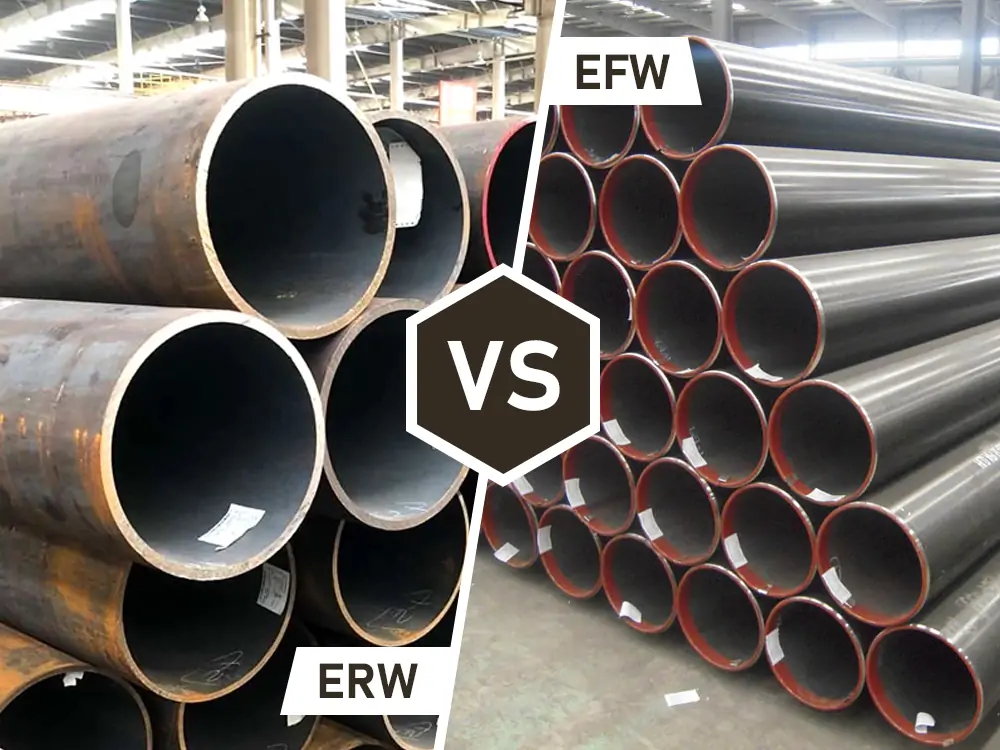
The differences in welded pipe varieties are mainly due to their varying manufacturing processes. In the pipe manufacturing and welding landscape, two manufacturing methods excel– ERW and EFW, producing ERW pipes and EFW pipes, respectively. The two methods may confuse you due to similar names and the electric welding involved in both manufacturing processes. However,…
Introduction Welded steel pipes are widely used in various industries. These pipes are also simply referred to as welded pipes, which have seams on their surfaces when steel plates or strip coils are rolled into cylindrical shapes. Simple production methods, such as ERW and SAW, are highly efficient and affordable. They can produce pipes for…
Introduction The standard reference of the square hollow section is the box steel or tube steel. The aesthetic appearance of steel tubing makes it ideal for construction. They are suitable for the manufacture of steel structures and machinery. The manufacturer prefers the use of hollow structural sections. They could improve structural integrity, cost efficiency, and…
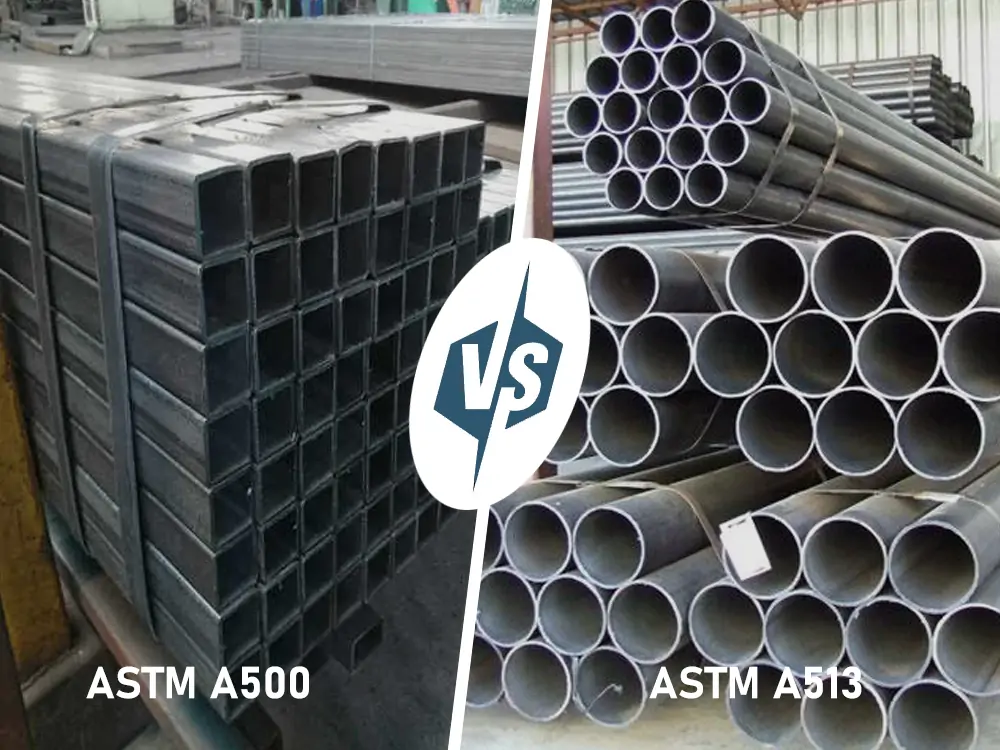
Introduction Steel tubing is a widely used engineering or structural material. Known for its strength and excellent performance, it is used in a wide range of applications, including construction and engineering projects. Two of the most common steel tubing specifications are ASTM A500 and A513. At first glance, they seem similar—both are typically ERW—but they…
Introduction Different industries in the market follow different specifications for pipes. API 5L is one of the most widely used standards for the manufacture of pipes. Such a specification ensures that pipelines are uniform in strength, durability, and safety. They must withstand the specific challenges in harsh conditions. These conditions are prevalent in situations encountered…
Introduction Carbon steel pipes stand as one of the main components of various industries, while you can find multiple types of carbon steel pipes in the market. Mainly made of carbon and iron, with minor quantities of other materials. The carbon content is 2.1% of the total alloy’s weight. Variations in steel pipes arise from…
Introduction There are trace amounts of elements in the steel pipes that increase the tensile strength. Carbon steel pipes have 0.02-2.1% by weight. Steel pipes are made from various metals and compounds. These compounds combine to form an alloy. Manufacturing industries use carbon steel pipes for construction and structural support. Other sectors use carbon-steel pipes,…
Introduction Manufacturers use steel pipes for modern infrastructure, automotive, and transport purposes. These pipes are powerful and can bear high temperatures and pressure. These pipes are used in skyscraper construction, deep pipelines, and other applications. The manufacturer designs different types of steel pipes to withstand specific conditions, whether moving fluids, bearing loads, or operating under…
Introduction The industrial use of ASTM A53 and ASTM A106 steel pipes makes them the most common types of carbon steel pipes. The carbon steel pipes comply with ASTM A53 and ASTM A106. They have wide applications in different sectors, because these pipes differ in their objectives, applications, and specifications. The significant difference between the…
Introduction Carbon steel is highly used in industries. A few of them are car manufacturing industries, machinery and tool manufacturing, as well as the construction industry, where carbon steel is used in their operations. It is important to remember that the largest constituent of this steel is carbon, the smaller parts of which are manganese,…
Introduction Boiler pipes are used in many industrial processes, such as chemical processing, oil refinery, and power production. Due to their resistance to high temperatures and pressures, these boiler pipes and tubes are used in environments with such conditions. The boiler pipes form the foundation of thermal systems in industries, facilitating the easy convection of…
When dealing with pipe systems, it is easy to confuse pipe schedules. It is important to understand the terminology, especially for engineers and contractors working on construction and industrial projects. This allows them to select the right pipe for the specific application, such as high-pressure handling or structural support. Are you curious to know about…
Introduction China is the largest producer and exporter of carbon steel pipes. It manufactures and sells these pipes in large quantities. The country supplies millions of tons of these products each year. They go to the construction, oil and gas, shipbuilding, and power generation industries. China is set to produce over 1 billion metric tons…
Introduction The global industries require seamless steel pipes that are valued due to their non-welded nature, strength, pressure resistance, and corrosion resistance. They find their way in the oil, natural gas, chemicals, power, and construction industries. The seamless steel pipe market worldwide has already surpassed the USD 100 billion mark and continues to record consistent growth….
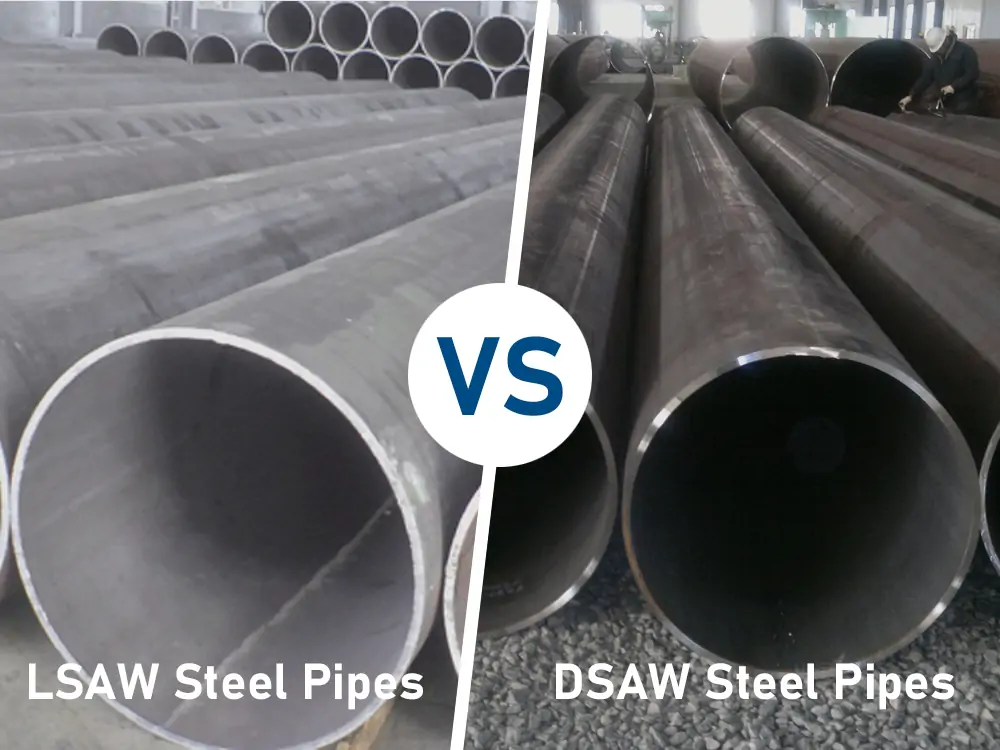
Introduction It isn’t easy to imagine how the oil and gas industry would function without the utility of steel pipes. They have an essential use in construction and structural engineering. Among the various pipe welding techniques in the industry, LSAW and DSAW steel pipes appear to hold a special place. This is because of the…
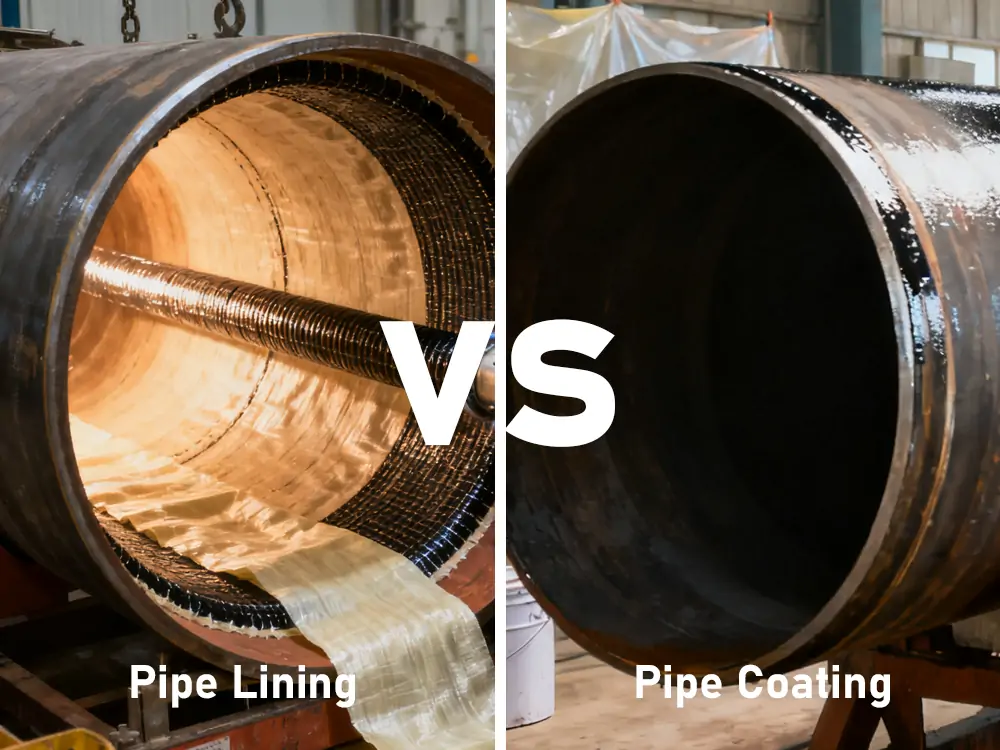
Introduction Corroded metal or carbon steel pipes are restored through processes known as pipe lining and pipe coating. The plumbing, water supply, gas supply and industrial processes are based on pipes. Pipes are also necessary for domestic use. Due to environmental changes, these pipes deteriorate through corrosion, abrasion, or exposure to chemicals. Although both techniques…
Many industries are using pipes that are made of carbon and carbon alloy. People are using these pipes to transport fluids and gases. Carbon steel pipes have high strength, which makes them suitable for use in construction, water systems, and even power plants. These pipes are durable, cheap, and resistant to damage. However, they have…