Introduction
The selection of the type of pipes is essential when constructing any system that uses pipes. Two standard options are Schedule 10 (Sch 10) and Schedule 40 (Sch 40). These pipes have numerous applications in plumbing, building, and construction, as well as in chemical plants and various industries.
These two types may seem similar on the outside. The primary distinctions between them are the wall thickness, weight, pressure capacity, and price. These are factors that influence how the pipes will function and at which location they can be placed.
This article first explains what Sch 40 pipe and Sch 10 pipe are, then goes on to describe the differences between them. Ultimately, it outlines the pros and cons of each pipe.
Whether you need to repair a small job at home or put up a giant industrial plant, the following article will help you know the kind of pipe most suitable for your project.
Understanding Pipe Schedules
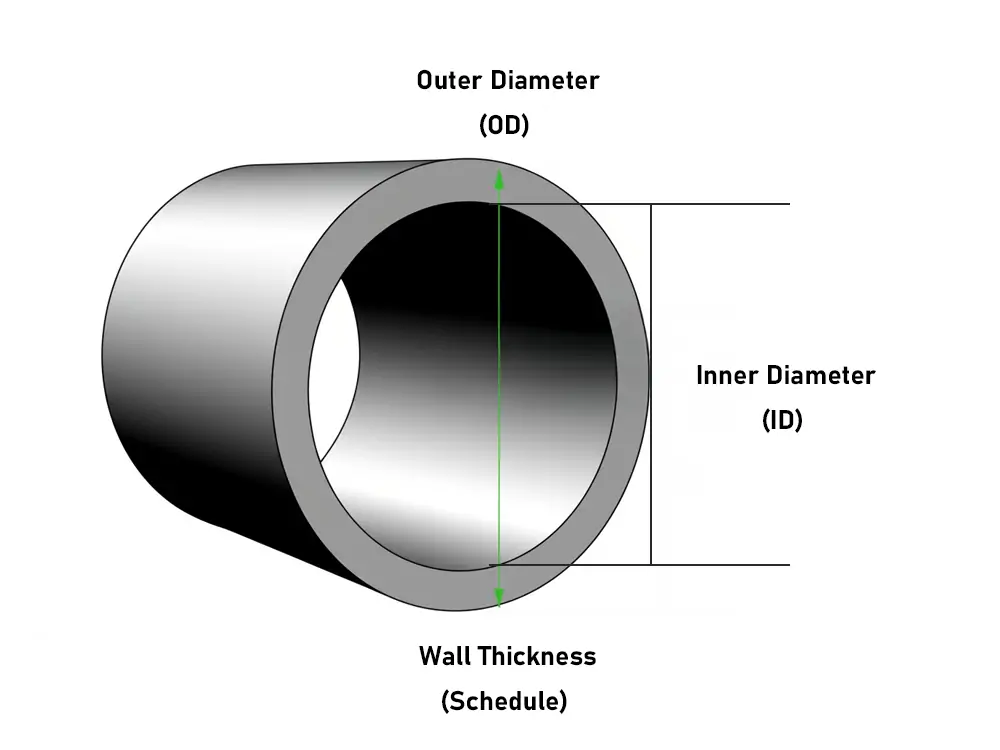
The term “schedule” in piping applications refers to the thickness of a pipe wall. It is written as “Sch” followed by a number, such as Sch 10 or Sch 40. The more the number, the thicker the wall of the pipe.
This system helps standardize the thickness of the pipes. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) introduced it to avoid confusion between metric and inch-based units of measurement. A schedule number can be used as an alternative to measuring thickness in millimeters or inches, etc.
The schedule number does not rely on the pipe’s length or outer diameter. It mentions the thickness of the wall only. Thicker walls allow the pipe to endure more pressure and increase its longevity.
Schedule 10 and Schedule 40 are among the most common pipe types. Sch 10 pipes have thinner walls. It makes them lighter and easier to handle, and they are often chosen for low-pressure applications. In contrast, Sch 40 pipes have thicker walls. It makes them stronger and more suitable for high-pressure jobs.
What is Schedule 10 Pipe?
Sch 10 pipe, also called schedule 10 pipe, is a pipe characterized by thin walls. It is less heavy and is handled efficiently. It is also less expensive to move and install since it is lighter in structure. This is the reason why it is generally applied in low-pressure systems.
This type of pipe is mainly composed of stainless steel, carbon steel, or PVC. They are best suited in a setting in which strength and durability are not key factors, but cost and convenience are more important.
What is Schedule 40 Pipe?
Schedule 40 pipe is a kind of piping characterized by thick walls and strong structure. It is stronger, more durable, and more suitable for medium- and high-pressure systems than Schedule 10 pipe since it has a thicker wall. These pipes are typically used where there is a need for the pipe to withstand higher pressure and physical stress.
The Sch 40 pipe is usually preferred when a long service life and resistance to physical and thermal stress are required. It is most suitable when price and weight are not as important as security, performance, and endurance.
Differences Between Schedule 10 and Schedule 40 Pipes

There are some differences between the Schedule 10 and Schedule 40 pipes. A few of them include wall thickness, pressure rating, weight, cost, and application. These are factors that determine the type of pipe that should be used in a particular work or environment.
Wall Thickness and Weight
The key distinction is the degree of wall thickness, which refers to the thickness of the pipe’s wall. The walls of schedule 10 pipes are thinner, thus lighter and easier to handle. Schedule 40 pipes are stronger, heavier, and more rigid due to their thicker walls.
This additional thickness makes Schedule 40 pipes more durable and able to withstand greater pressures, but it also increases their difficulty to cut, bend, and carry.
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Sch 10 Thickness (mm) | Sch 40 Thickness (mm) |
| 1/2 inch | 1.65 | 2.77 |
| 1 inch | 1.65 | 3.38 |
| 2 inch | 2.11 | 3.91 |
| 4 inch | 2.77 | 6.02 |
| 6 inch | 2.77 | 7.11 |
| 8 inch | 3.05 | 8.18 |
| 10 inch | 3.40 | 9.27 |
| 12 inch | 3.96 | 10.31 |
Pressure Ratings
Another very important factor to consider when discussing the differences between pipes is the pressure at which the pipe may explode.
The Schedule 40 pipes can withstand much more pressure due to their thicker walls. Schedule 10 pipes are intended for use in low- or medium-pressure systems only and should not be used in challenging applications.
Below are the pressures of Schedule 10 and 40 pipes:
● Schedule 10
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Material | Pressure Rating (psi) |
| 1/2 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 230 |
| 1 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 230 |
| 2 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 230 |
| 4 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 230 |
● Schedule 40
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Material | Pressure Rating (psi) |
| 1/2 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 1670 |
| 1/2 inch | Carbon Steel (A53 Grade B) | 1575 |
| 1 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 1440 |
| 1 inch | Carbon Steel (A53 Grade B) | 1575 |
| 2 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 1090 |
| 2 inch | Carbon Steel (A53 Grade B) | 1300 |
| 4 inch | Stainless Steel (A312-TP316/316L) | 870 |
| 4 inch | Carbon Steel (A53 Grade B) | 1000 |
Cost
Sch 10 pipes are usually cheaper since they consume a smaller amount of material as compared to pipes of Sch 40. Moreover, its lightweight lowers the cost of labor and shipping.
Sch 40 pipes are thicker, as they require more material and are more expensive. They are powerful and have excellent pressure resistance, particularly in critical installations.
Sch 10 is a cost-effective product to use in projects that do not involve high pressure. For Sch 40, the higher price is worth it in applications where greater strength and safety are needed. During the project purchase, buyers are advised to consider the project’s needs in relation to the price to avoid excessive budget consumption or the risk of poor-quality pipes.
Installation and Handling
Sch 10 is lighter, can be easily cut, bent, and installed. Therefore, it reduces labor, installation, and shipping costs. It also benefits the construction industry, whose jobs often require rapid completion and materials must be managed efficiently, such as in small projects or residential houses.
Sch 40 costs more, takes longer and is harder to deal with since it is more difficult to move around, cut and weld. They may require specialized equipment, including pipe clamps, conveyors, and lifters. They are, however, stronger and are employed in systems that require a more robust structure.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
All types of pipes have different purposes. Schedule 10 is most appropriate in low-pressure and non-critical applications, such as light-duty operations. Sch 40 is applied in cases where durability, resistance to pressure, and strength are required.
| Application Area | Sch 10 Uses | Sch 40 Uses |
| Water Systems | Low-pressure water distribution, sprinkler systems | Plumbing, high-pressure water lines |
| Gas and Oil | Not suitable for high-pressure gas/oil transport | Gas pipelines, oil transportation lines |
| Industrial | Ventilation ducts, non-critical fluid transport | Chemical processing, high-pressure industrial lines |
| Irrigation | Lightweight irrigation systems | Heavy-duty irrigation systems |
| Structural | Weak load-carrying building structures | Structural supports, mechanical uses |
| HVAC | Exhaust systems, drainage lines | Ducts, pipes and high-temperature fluid systems |
Pros and Cons Comparison
This section highlights the advantages and disadvantages of Schedule 10 pipe and Schedule 40 pipe, allowing you to select the most suitable option based on your specific requirements, including pressure, cost, ease of installation, and durability.
SCH 10 Pipes
Pros:
- Lighter and more manageable
- More reasonably priced
- Ideal for applications requiring little pressure
- Simpler to transport and install
Cons:
- Not enough to use in high-pressure applications
- Too weak to be of heavy-duty use
- Only the non-essential applications
SCH 40 Pipes
Pros:
- Stronger and durable
- Ideal in applications that need high pressure
- Better for plumbing and industrial systems
Cons:
- Heavier and challenging to manage
- More costly
- More work is needed to install
Conclusion
You will need to make the right selection of pipe schedule to ensure your piping system operates optimally. The Sch 10 and Sch 40 pipes might have a similar look, but they are used differently.
Schedule 10 pipes are inexpensive, easy to install, and lightweight. Its features make it perfect for low-pressure systems or where the pressure factor is not a significant concern. They are commonly used in systems such as ventilation, drainage, or sprinkler systems.
Sch 40 pipes, however, are stronger and built to support higher pressure. They are normally utilized in systems that require more pressure, such as plumbing, gas and oil pipelines, and heavy industries. The Sch 40 pipes are more expensive and heavier. They require a lot of work to be installed compared to Schedule 10 pipes.
Consider the project’s circumstances before selecting a schedule type. The schedule 10 pipes would be better in cases where low cost is a priority and the system does not require high pressure. However, in cases where a project involves higher pressure or a more stringent set of requirements, then Sch 40 pipes would be a more reliable choice.
By understanding the primary distinction between these two pipes, you will find yourself in a better position to choose the kind of piping to design, construct or repair. If you are looking for a stronger steel pipe, you can choose Sch80 pipes. Click here to see the difference between Sch 40 and Sch 80 pipe.
