
Carbon steel pipes are widely used in almost every other industry. They are made in different types and grades to suit diverse industrial needs. Due to their strength, high-pressure capacity, and durability carbon steel pipe is used in high-demanding industries like oil and gas, construction, and mechanical engineering.
Carbon steel pipes are categorized depending on their manufacturing process, uses, and grade.
In this article, we will discuss the carbon steel pipe types, manufacturing process and applications. We will explain its manufacturing process uses and answer some pertinent questions about carbon steel pipe making.
Let’s understand how steel pipe is made.
Carbon Steel Pipe Manufacturing
Carbon steel pipes are manufactured using seamless pipes and welded pipes. Both are different not only in manufacturing, price, properties and uses.
Seamless Pipes are made from a single piece of steel without any seams or joints, while welded pipes are made by joining two or more steel pieces together by welding.
Both are durable but seamless pipes lack weld points and joints; which makes them high-pressure resistant and uniform in structure. Welded pipes are also strong and durable, but weak points or joints may cause some defects or weak seams.
Let’s see how both carbon steel pipes are manufactured; we will explain the manufacturing process of both types.
Material Preparation
The process of carbon steel pipe starts with material preparation. Steel is the primary material in its manufacturing, but other alloys can exist depending on the type of pipe. In carbon steel, the primary alloying elements are carbon and steel.
The carbon steel pipe-making process starts with heating and making iron ingots and combining it with coke.
Coke is a carbon-rich substance made by heating coal in the absence of air and removing most of the carbon by blasting it with oxygen. Molten steel with carbon is poured into a large iron mold, forming steel ingots.
Once shaped like sheets, tubes, or pipes, these ingots are the starting material in pipe manufacturing.
Ingots are further shaped into bloom or slabs depending on the type of carbon steel pipe manufacturers are making.
● Bloom
Ingots are passed through a rigorous rolling process. High-mill rollers are mounted on opposite grooves and move in opposite directions.
The rolling stretched and squeezed ingots into long, thin pieces. The rollers pull back the steel ingots from both sides. A manipulator periodically flips the steel during this process to ensure uniform structure.
The process is repeated until iron ingots are formed into blooms that serve as raw pipe-making material. When steel acquires the desired shape, it is cut into shorter pieces.
● Slab
The process of slab-making is similar to the bloom. The ingots are passed through stacked rollers, which stretch them. Some rollers on the side ensure the consistency of the slab thickness. The process continues until steel acquires the desired shape, and its uneven ends are cut to give a uniform shape. Slabs are heated to 22,000 C0, causing them to form an oxide coating on their surface.
This coating is removed through high-pressure water spray and a scale breaker. The slabs are made into thin, narrow, longer strips called skelp. The process converts a 6-inch slab into a quarter-mile-long thin strip.
After stretching, both bloom and slab are pickled. Pickling is running the pieces into tanks containing sulphuric acid to clean. Once the metal is clean, it is washed with hot and cold water and stacked neatly for pipe making.
Types of Carbon Steel Pipe
Welded Pipes
As we have mentioned, welded pipes are made from skelps. Skelps are cut into desired lengths. The steel skelp is heated and passed through a roller, which curls up the ends and shapes them into the pipe. Even welded pipes come in three distinct types, and their manufacturing differs.
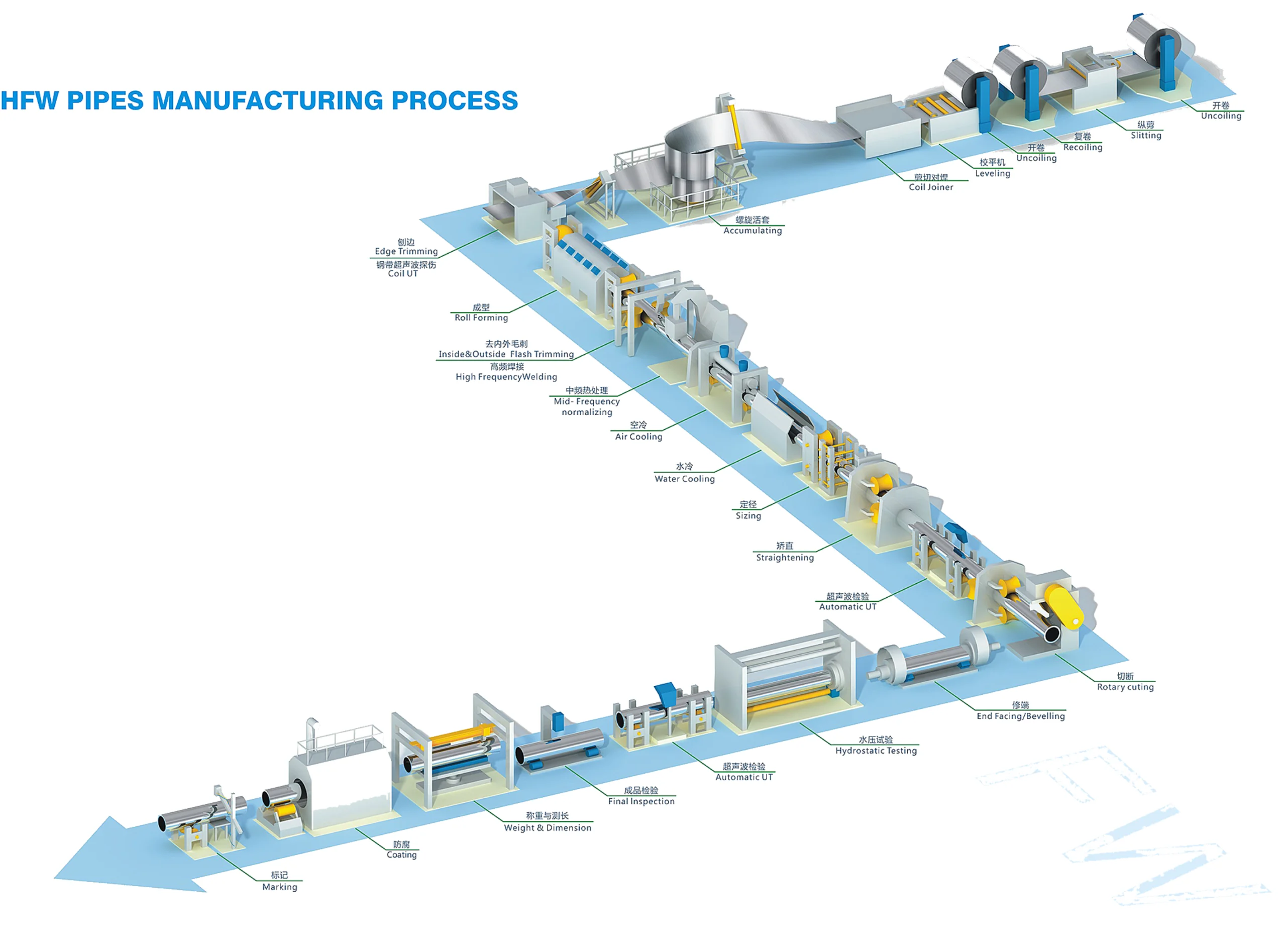
1. Electric Resistance Welding (ERW)
The steel skelp is melted and passed through rollers, which curl up their ends and form them into a pipe shape. The pipe is further passed through a welding process where electrodes are passed. The metal resists the current and is melted, forming the welded pool. The edges come into contact and as the steel solidifies, two ends are joined.
2. Longitude Submerged arc welding (LSAW)
This type of pipe is formed from steel plates and has a larger diameter than 24 inches with high wall thickness. In this process, the weld and arc are submerged under fusible flux.
3. High-Frequency Induction Welding
It works almost like electric resistance welding but uses an induction coil to initiate the current. HFI pipes are used in the oil and gas industry because of their strong weld quality.
Seamless Steel Pipe
Seamless pipes are made from billets, which are melted and molded into round shapes and are called rounds. Rounds are further heated until white in the furnace and rolled under high pressure.
The heated round is further rolled, causing it to stretch outside and forming a hole inside like the shape of a pipe. A bullet-shaped piercing point is passed through the rolling rounds to form a uniform and exact hole. Still, the shape can be irregular until passed through a series of rollers until it forms a standard outside diameter and controlled thickness of walls.
After making both types of pipe, they are put through a processing machine. They may also be attached to joints for joining two or more pipes. The machine stencils the data and information relating to the pipe on it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=67&v=B1gcSyqLkA0&embeds_referring_euri=https%3A%2F%2Funiasen.com%2F&source_ve_path=MjM4NTE&feature=emb_title
Quality Control and Inspection
To ensure the consistency of quality, diameter, and thickness of wall carbon steel pipe has to go through several tests and inspections after manufacturing.
Despite the mechanical testing and visual inspection, the pipes are passed through measuring machines. These machines check the diameter and thickness of the wall.
Finished metal pipes are further inspected using X-ray machines to ensure quality and precision.
Special X-ray machines are used to inspect the diameter, thickness of the wall, and its consistency. X-rays are monitored to ensure the thickness meets the standards, and they can also reflect the deformities and internal defects in weld if there are some.
Final Processing
Even after manufacturing, carbon steel pipes are not ready. They require post-processing to make sure they are corrosion and oxidation-resistant.
Post-processing includes surface cleaning. Carbon steel pipes are coated with different materials to make them corrosion resistant, and some of the types of coating are
Black lacquer is use gives a black or dark finish to black carbon steel pipe. It protects pipes from corrosion and atmospheric corrosion.
Applying layers of oil also prevents corrosion and oxidation processes. It creates a barrier between steel and oxygen. Besides oils, varnish, or epoxy coatings are applied to steel pipes. Steel Pipes are also immersed in a bath of molten zinc to make them highly corrosion-resistant.
Besides these, several other standards practice different coatings depending on the type of steel, pipe, and industrial uses. Not only do these finishes give more strength to pipes, but they make them durable and aesthetically appealing.
Delivery
After the final processing, pipes are meticulously inspected to ensure quality of coating and pipes. They are packed in wooden, plastic, or steel crates neatly stacked with special pipe protectors.
A well-coordinated logistics and transportation system is linked to deliver the pipes to their destinations. The storage, transportation, and delivery process is planned to ensure the pipes reach their destination safely.
Carbon Steel Pipe Applications

Carbon pipes are used in several industries, including oil, gas, construction, steel fabrication, metal industry, and mechanical engineering, to name a few.
The application of these pipes depends on their type, construction, size, and material. For example, seamless pipes are more expensive as compared to welded pipes. They are used in industries where higher precision and strength of pipe are required.
They can withstand high pressure as compared to welded pipes. The lack of welded joints means they have fewer pressure points. They are used in the oil and gas, power generation, construction, and infrastructural industries in building big bridges and buildings.
Welded pipes may have weak welded joints. They are used in industries where less pressure resistance is required. Industries like water supply, distribution piling, and foundation support in mechanical engineering fencing or pressure piping systems that use welded pipes. They are also used in the industrial and manufacturing industries.
Conclusion
Carbon steel pipes are the backbone of almost every industry. Carbon steel manufacturing is a complex procedure requiring all stages of monitoring and care. Due to high-quality technology in carbon steel making and maintaining quality assurance, pipes are made durable, strong, and pressure-resistant. The use and demand of these pipes across industries are growing.
Uniasen is one of the best carbon steel suppliers in the world. We have extensively provided quality steel l products, including Pipes like ERW steel pipes, Seamless pipes, hollow pipe, coatings, and fittings worldwide. We provide all types of carbon steel pipes, maintaining high standards in quality and performance to our customers. The industry has diverse customers.
